SATA and M.2 Solid-State Drive FAQs
All your SSD questions answered
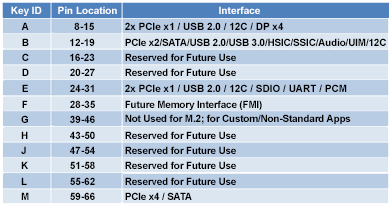
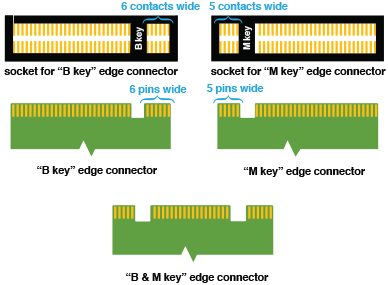
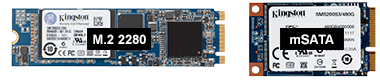
Kingston solid-state drives are the ideal performance upgrade for consumers and organizations alike. Available in a wide range of models and capacities, Kingston SSDs extend the lifecycle of PCs and provide improved speed, performance and reliability when compared to traditional hard drives.
Backed by a two-, three- or five-year warranty, free technical support and legendary Kingston® reliability, Kingston solid-state drives provide data security combined with future-proof performance for complete peace of mind.
If you have any questions about Kingston solid-state drives, read on for the answers. If your question isn’t covered here, please visit the product pages listed below or contact a Kingston representative.