SSD KC2000 NVMe PCIe - サポート
リソース
ビデオ
よく寄せられる質問
1. https://www.kingston.com/support/technical/ssdmanager から Kingston SSD Manager をダウンロードして、ご使用のドライブで利用可能なファームウェアアップデートがあるかどうかを確認し、ある場合はアップデートを適用します (推奨される場合)。
2. システムメーカーのサポートページを参照して、システムで利用可能な BIOS アップデートがあるかどうかを確認します。
3. OS の最新バージョンを実行していることを確認し、保留中のアップデートがないことを確認します。
4. お使いのシステムの最新ドライバーが動作していることを確認します。これは、システムメーカーのサポートページにアクセスし、最新のドライバーアップデートを探すことで可能です。
これらの手順を実行してもまだシステムに問題がある場合は、Kingston テクニカルサポートにお問い合わせください。
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-21
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
内蔵型SSDや外付けUSBなどのフラッシュストレージではよくあることで、フラッシュメモリのメーカーと、回転するプラッタ製ハードドライブメーカーのメガバイトの計算方法が異なるため、このようなことが起こります。ハードドライブメーカーはメガバイト(または1,000x1,000バイト)を1,000KBととして計算するのに対し、フラッシュベースのストレージでは二進法を用い1,024KBとして計算します。
例:フラッシュベースのストレージデバイスが1TBの場合、Windowsでは931.32GBの容量として計算されます。(1,000,000,000,000÷1,024÷1,024÷1,024=931.32GB).
さらに、Kingstonではフォーマットやファームウェアおよび/または操作に関する情報などの機能のために、製品に表記された容量の一部を予約として使用しています。このことから、製品に表記された容量の一部はデータストレージとして使用できません。
FAQ: KDT-010611-GEN-06
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
注意:サーマルスロットリングは、SMART 温度が 80°Cに達すると動作します。
FAQ: KSD-060117-NVME-02
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
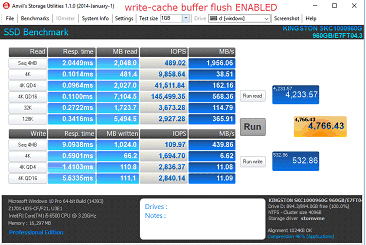
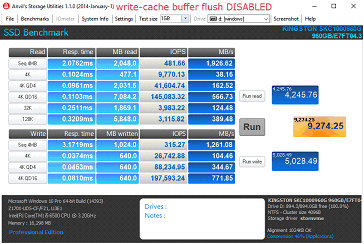
Write-Cache Buffer Flush (ライトキャッシュ・バッファーフラッシュ機能) を無効にする手順
1. デバイスマネージャを開きます。
2. ディスクドライブを選択して開き、次にターゲットドライブを選択します。
3. 右クリックして、「プロパティ」を選択します。
4. "Turn off Windows write-cache buffer flushing on the device" (デバイスに対する Windows のライトキャッシュ・バッファーフラッシュ機能をオフにする) をチェックします。
a. 注意:デバイスで書込みキャッシュバッファーのフラッシュを無効にすると、停電が起きた場合に転送中のデータの損失またはデータの破損、あるいはその両方のリスクを負うことになります。関連するリスクをご承知された場合のみ、この機能を無効化してください。
パフォーマンスの比較
FAQ: KSD-060117-KC1000-04
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
FAQ: KSD-060117-NVME-01
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
FAQ: KSD-001525-001-00
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
これが不可能な場合、または以前のデータを新しいドライブにクローンした場合は、システム BIOS で新しいドライブが起動デバイスとして表示されることを確認し、起動用に選択します。
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-03
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/topic/update-to-add-native-driver-support-in-nvm-express-in-windows-7-and-windows-server-2008-r2-03cd423b-d42e-66c2-722b-019d16455a6b
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-06
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-07
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
BIOS にドライブが存在する場合は、オペレーティングシステム内でディスクを初期化する必要がある場合があります。
Windows の場合:
ステップ 1:ドライブが正しく接続されていることを確認し、システムの電源を入れ、Windows OS を起動します。
ステップ 2:Windows + X を押し、ディスクの管理を選択します。
ステップ 3:SSD が新しく初期化されていない場合、「ディスクを初期化してください」というポップアップが表示されます。
ステップ 4:次のいずれかを選択します。
MBR(マスターブートレコード):2TB 未満のドライブや古いシステムに適しています。
GPT (GUID パーティションテーブル):最新のシステムや 2TB 以上のドライブにおすすめです。
ステップ 5:「OK」をクリックしてディスクを初期化します。
ステップ 6:初期化されると、SSD が「未割り当て」と表示されます。その上で右クリックし、「新しいシンプルボリューム」を選択します。
ステップ 7:画面の指示に従って SSD をフォーマットし、ドライブ文字を割り当てます。
Mac OS の場合:
ステップ 1:ドライブが正しく接続されていることを確認し、システムの電源を入れ、Mac OS を起動します。
ステップ 2:ディスクユーティリティを開きます (Spotlight で Cmd + Space と入力し、「ディスクユーティリティ」と入力すると見つかります)。
ステップ 3:左側のペインで SSD を選択します。
ステップ 4:「消去」をクリックします。
ステップ 5:ドライブの名前を入力し、「フォーマット」で以下を選択します。
新しい Mac および SSD の場合は、APFS。
古いシステムや HDD の場合は、Mac OS Extended(ジャーナル付き)。
ステップ 6:「消去」をクリックします。プロセスが完了すると、SSD が使用可能になります。
Linux の場合:
ステップ 1:ドライブが正しく接続されていることを確認し、システムの電源を入れ、Linux OS を起動します。
ステップ 2:ターミナルを開きます。
ステップ 3:sudo fdisk -l と入力し、接続されているすべてのドライブをリストアップします。SSD のサイズを確認し、デバイス名 (例:/dev/sdb) をメモします。
ステップ 4:fdisk または parted を使って SSD を初期化します。以下は fdisk を使った基本的なガイドです。
sudo fdisk /dev/sdb (/dev/sdb を SSD のデバイス名に置き換えてください) と入力します。
g を押して新しい GPT パーティションテーブルを作成します。
n を押して新しいパーティションを作成します。プロンプトに従ってサイズとタイプを指定します。
w を押して変更を書き込みます。
ステップ 5:SSD 上の新しいパーティションをフォーマットします (例:/dev/sdb1)。お好みのファイルシステムでフォーマットできます。
ext4 の場合:sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
ext3 の場合:sudo mkfs.ext3 /dev/sdb1
FAT32 の場合:sudo mkfs.vfat /dev/sdb1
ステップ 6:SSD をマウントします。
マウントポイントを作成します:sudo mkdir /mnt/myssd
SSD をマウントします:sudo mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/myssd
忘れずに、dev/sdb1 を SSD のパーティション名に置き換えてください。
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-15
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
https://www.kingston.com/blog/pc-performance/two-types-m2-vs-ssd
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-16
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-18
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
Linux の完全消去ガイド
このガイドでは、Linux ツールを使用して Kingston SSD を安全に消去する方法を、ステップごとに説明します。
SATA 完全消去手順
警告
この先に進む前に、必ず重要なデータをすべてバックアップしてください。
前提条件
- ルート権限を持っている必要があります。
- SSD をセカンダリ(OS 以外)ドライブとして、システムに接続する必要があります。
- lsscsi と hdparm をインストールしておく必要があります。お使いのディストリビューションのパッケージマネージャーを用いてインストールする必要があります。
- ドライブがセキュリティフリーズされていないようにしてください。
- ドライブがパスワード保護されていないようにしてください。
手順
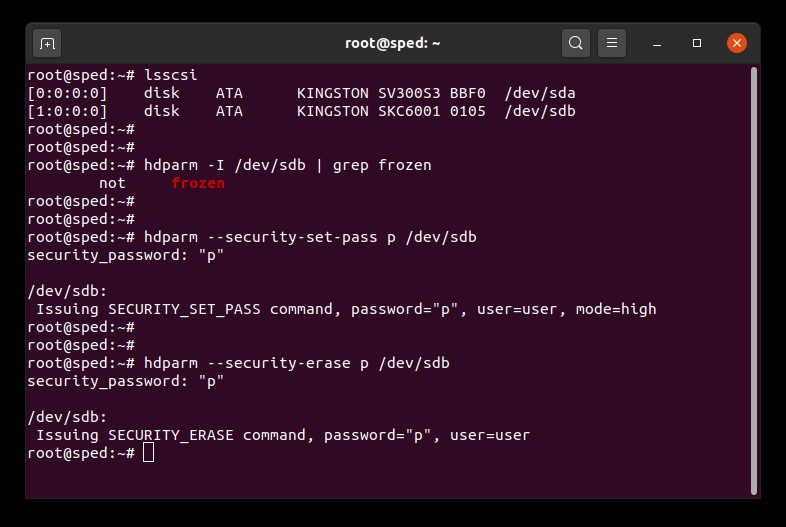
1.消去したいドライブのデバイス名(/dev/sdX)を調べます。
#lsscsi2.ドライブセキュリティがフリーズされていないことを確認します。
# hdparm -I /dev/sdX | grep frozen出力で(「not frozen」でなく)「frozen」と表示された場合は、次のステップに進めません。次の方法のひとつを試して、セキュリティフリーズを外す必要があります。
方法 1:
システムをスリープ状態(RAM へのサスペンド)にしてから、スリープ解除します。ほとんどのディストリビューションで、サスペンドするコマンドは次のとおりです。
# systemctl suspendここで hdparm コマンドをもう一度実行します。成功した場合、(「frozen」ではなく)「not frozen」が表示されます。
方法 2:
ドライブをホットプラグします。これは、SATA の電源ケーブルを物理的にドライブから引き抜き、システムの電源が入っている間にもう一度差し込みば行なえます。BIOS でホットプラグを有効にしておく必要があります。システムによっては、ホットプラグをサポートしないものもあります。 ここで hdparm コマンドをもう一度実行します。成功した場合、(「frozen」ではなく)「not frozen」が表示されます。
3.ドライブにユーザーパスワードを設定します。パスワードは何でもかまいません。この例ではパスワードを「p」に設定します。
# hdparm --security-set-pass p /dev/sdX4.同じパスワードを使用して、ドライブに完全消去コマンドを実行します。1234567890 - 1234567890 -
# hdparm --security-erase p /dev/sdXこのコマンドは完了するまでに数分かかります。正常に完了するとドライブパスワードが除去されます。
完全消去が中断された場合や、その他の失敗が起こった場合は、ドライブにセキュリティロックがかかります。この場合、下のコマンドを使用してセキュリティロックを外し、完全消去手順を再び試すことができます。
# hdparm --security-disable p /dev/sdXSATA 完全消去の例
NVMe 完全消去手順
警告
この先に進む前に、必ず重要なデータをすべてバックアップしてください。
前提条件
- ルート権限を持っている必要があります。
- SSD をセカンダリ(OS 以外)ドライブとして、システムに接続する必要があります。
- nvme-cli をインストールしておく必要があります。お使いのディストリビューションのパッケージマネージャーを用いてインストールしておく必要があります。
- ドライブがパスワード保護されていないようにしてください。
手順
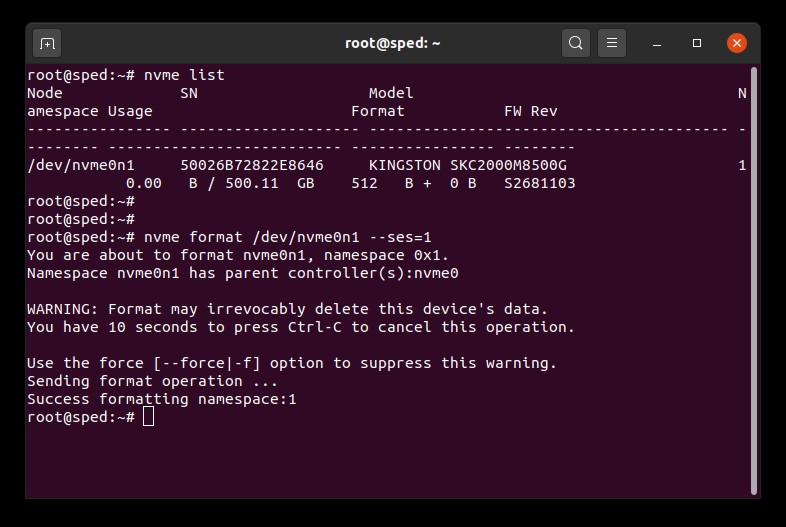
1.消去したいドライブのデバイス名(/dev/nvmeXn1)を調べます。
# nvme list2.ドライブのフォーマットコマンドを実行します。ここで、完全消去設定を 1 に設定します。これは、ユーザーデータ消去を示します。
# nvme format /dev/nvmeXn1 --ses=1このコマンドは完了するまでに数分かかります。
NVMe 完全消去の例
FAQ: KSM-SE-LIX
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
SSD に新しいファームウェアが必要な場合は、ここにある Kingston の SSD Manager ソフトウェアを実行すると通知が表示されます。 www.kingston.com/ssdmanager
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-11
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
TRIMとガベージコレクションは、最新のSSDに組み込まれたパフォーマンスと耐久性を向上するテクノロジーです。SSDをパッケージから取り出したときはNANDブロックがすべて空になっており、SSDは単一処理でこれらの空ブロックに新しいデータを書き込むことができます。いずれ、これら空ブロックのほとんどはユーザーデータを含む使用済みブロックとなっていきます。使用済みブロックには、SSDが新しいデータを書き込むため、読み取り、修正、書き込みのサイクルを強制実行します。こうした読み取り、修正、書き込みのサイクルは3つの処理を実行しなければならないのでSSDの全体的なパフォーマンスに負担がかかります。読み取り、修正、書き込みのサイクルは書き込み増幅の原因にもなり、SSDの全体的な耐久性にも重負荷を課します。
TRIMとガベージコレクションは、相互に連動して使用済みブロックにスペースを確保するのでSSDのパフォーマンスと耐久性を向上させます。ガベージコレクションはSSDコントローラに組み込まれている機能であり、使用済みブロックに保存されたデータを統合して、書き込み可能なスペースを設けます。こうした処理はSSDが完全にバックグラウンドで実行します。ただし、SSDはどのブロックにユーザーデータが含まれ、どのブロックのデータをユーザーが削除したのか見分けることができません。その処理をするのがTRIMです。TRIMは、データが削除されたときにオペレーティングシステムに認識させ、使用済みブロックを再利用できるようにします。これを可能にするには、オペレーティングシステムとSSDの両方がTRIMをサポートする必要があります。最新のオペレーティングシステムとSSDはTRIMをサポートしますが、RAID構成のほとんどはサポートしていません。
Kingston SSDはTRIMとガベージコレクションの両方を取り入れており、SSDのライフサイクルにわたって最大限可能なパフォーマンスを耐久性を維持します。
FAQ: KSD-011411-GEN-13
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
M.2 は物理的なフォームファクタですが、SATA と PCIe はストレージインターフェースを指します。主な違いは M.2 SSD で実現されるパフォーマンスとプロトコル (言語) です。
M.2 仕様は SSD 向けに SATA と PCIe の両方のインターフェースを対象とします。M.2 SATA SSD は現在、代表的な 2.5 インチの SATA SSD にあるコントローラーと同じものを使用します。一方、M.2 PCIe SSD は PCIe プロトコル専用のコントローラを使用します。M.2 SSD は 1 つのプロトコルしか対応できませんが、システムによっては SATA か PCIe のいずれかに対応する M.2 ソケットが装備されているものもあります。
FAQ: KSD-004005-001-00
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
「静電気の放電」の短縮形で、ESD とは帯電した静電気の放電のことです。 ESD は、各個人がパソコンやハードウェアコンポーネントを損傷または破壊させる可能性のある現象の一つであるため、決して軽視すべきではありません。 あなたがカーペットの上で足を擦った時や、何らかの金属に触れた時に、静電気の放電が起こります。 ESD はユーザーが感電したことを感じないで発生する場合があり、またパソコン内部の作業している時やハードウェアを取り扱っている時に起こります。
ESD を防ぐ方法
ESD を防止する最良の方法は、接地用のリストストラップを着用するか、またはマットやテーブルの接地を行うことです。 しかし、ほとんどのユーザーはこれらのアイテムを使わないため、当社は ESD をできるだけ低減するために役立つ手順を以下に示します。
- 立って作業する – パソコンで作業する時は、常に立ったまま作業するように推奨します。イスに座ると、静電気の発生量が増加します。
- 各種コード - パソコンの背面の接続ケーブル (電源ケーブル、マウスケーブル、キーボードのケーブルなど) をすべて外してください。
- 服装 - ウールのセーターなどの静電気が帯電しやすい服を着ないようにしてください。
- アクセサリ - ESD の低減や、その他の問題の防止に役立つ良い方法の一つは、身に付けているすべての宝飾品を外すことです。
- 天候 - 落雷は ESD のリスクを高めます。落雷が起こっている時は、絶対に必要な場合を除き、パソコンでの作業を行わないようにしてください。 非常に乾燥した地域では、絶縁された表面を流れる (風、エアコン、扇風機/換気扇からの) 気流が発生すると、空気そのものが静電気の発生機構になります。 湿度を高くして静電気の放電を防ぐという考えは間違っており、接続部や他の電気的なインタフェースでの腐食の問題に留意してください。
ESD の詳細や、お手元の電子部品を保護する方法については、以下のサイトをご覧ください。
ESD Association
https://www.esda.org
FAQ: KTC-Gen-ESD
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
https://www.kingston.com/blog/pc-performance/nvme-vs-sata
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-19
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
1.最初に、データをバックアップすることをおすすめします。
2.次にセカンダリシステムを使用して、ドライブラベル上の PSID を使用して REVERT (取り消し)を完了します。注:REVERT を実行すると、ドライブ上のすべてのデータを安全に消去できます。
3.IEEE 1667 サポートを無効にします。
4.KSM をリフレッシュまたはリスタートすると、ファームウェアアップデートを使用できるようになります。
FAQ: KSM-001125-001-01
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
FAQ: KSM-001125-001-00
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
FAQ: KSM-001125-002-01
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
次の代替方法を使うと RST RAID が壊れますので、データ損失のおそれがあります。システムに RST RAID アレイがある場合、別の方法を試してください。
代替方法 1:BIOS で RST Control (RST 制御)を無効にします
このワークアラウンドには、RST Control を有効または無効にする BIOS オプションが必要ですが、使用できないシステムもあります。
注:この先に進む前にすべての重要データをバックアップしてください。
- 再起動してシステム BIOS に進みます。
- BIOS の RST Configuration (RST 構成)設定を探します。
- 「RST Controlled」を「Not RST Controlled」に変更します。
- 保存して BIOS を終了します。
- KSM を開き、ドライブファームウェアをアップデートします。
このステップが完了したら、BIOS で「RST Controlled」に戻してもかまいません。
代替方法 2:BIOS で RAID から AHCI に切り替えます。
このワークアラウンドはシステムストレージモードを RAID から AHCI に変更します。
すべてのシステムで実行可能です。
注:この先に進む前にすべての重要データをバックアップしてください。
- msconfig をオープンします
- 「Boot」(ブート)タブを選択します
- 「Safe boot - Minimal」(セーフ ブート - 最小)をチェックします
- OK をクリックして再起動します
- システムが再起動したら、システム BIOS に進みます
- ストレージモードを RAID から AHCI に変更します
- 保存して BIOS を終了します。
- Windows がセーフモードで起動するまで待ちます
- msconfig をオープンします
- 「Boot」(ブート)タブを選択します
- 「Safe boot」(セーフ ブート)のチェックを外します
- OK をクリックして再起動します
- Windows が通常の起動をするまで待ちます
- KSM を開き、ドライブファームウェアをアップデートします
このステップが完了したら、BIOS でストレージモードを RAID に戻してもかまいません。
FAQ: KSD-001525-001-01
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-04
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
SSD に新しいファームウェアが必要な場合は、ここにある Kingston の SSD Manager ソフトウェアを実行すると通知が表示されます。 www.kingston.com/ssdmanager
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-11
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-12
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-13
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-14
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-04
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-18
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
https://www.kingston.com/blog/pc-performance/two-types-m2-vs-ssd
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-16
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
BIOS にドライブが存在する場合は、オペレーティングシステム内でディスクを初期化する必要がある場合があります。
Windows の場合:
ステップ 1:ドライブが正しく接続されていることを確認し、システムの電源を入れ、Windows OS を起動します。
ステップ 2:Windows + X を押し、ディスクの管理を選択します。
ステップ 3:SSD が新しく初期化されていない場合、「ディスクを初期化してください」というポップアップが表示されます。
ステップ 4:次のいずれかを選択します。
MBR(マスターブートレコード):2TB 未満のドライブや古いシステムに適しています。
GPT (GUID パーティションテーブル):最新のシステムや 2TB 以上のドライブにおすすめです。
ステップ 5:「OK」をクリックしてディスクを初期化します。
ステップ 6:初期化されると、SSD が「未割り当て」と表示されます。その上で右クリックし、「新しいシンプルボリューム」を選択します。
ステップ 7:画面の指示に従って SSD をフォーマットし、ドライブ文字を割り当てます。
Mac OS の場合:
ステップ 1:ドライブが正しく接続されていることを確認し、システムの電源を入れ、Mac OS を起動します。
ステップ 2:ディスクユーティリティを開きます (Spotlight で Cmd + Space と入力し、「ディスクユーティリティ」と入力すると見つかります)。
ステップ 3:左側のペインで SSD を選択します。
ステップ 4:「消去」をクリックします。
ステップ 5:ドライブの名前を入力し、「フォーマット」で以下を選択します。
新しい Mac および SSD の場合は、APFS。
古いシステムや HDD の場合は、Mac OS Extended(ジャーナル付き)。
ステップ 6:「消去」をクリックします。プロセスが完了すると、SSD が使用可能になります。
Linux の場合:
ステップ 1:ドライブが正しく接続されていることを確認し、システムの電源を入れ、Linux OS を起動します。
ステップ 2:ターミナルを開きます。
ステップ 3:sudo fdisk -l と入力し、接続されているすべてのドライブをリストアップします。SSD のサイズを確認し、デバイス名 (例:/dev/sdb) をメモします。
ステップ 4:fdisk または parted を使って SSD を初期化します。以下は fdisk を使った基本的なガイドです。
sudo fdisk /dev/sdb (/dev/sdb を SSD のデバイス名に置き換えてください) と入力します。
g を押して新しい GPT パーティションテーブルを作成します。
n を押して新しいパーティションを作成します。プロンプトに従ってサイズとタイプを指定します。
w を押して変更を書き込みます。
ステップ 5:SSD 上の新しいパーティションをフォーマットします (例:/dev/sdb1)。お好みのファイルシステムでフォーマットできます。
ext4 の場合:sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
ext3 の場合:sudo mkfs.ext3 /dev/sdb1
FAT32 の場合:sudo mkfs.vfat /dev/sdb1
ステップ 6:SSD をマウントします。
マウントポイントを作成します:sudo mkdir /mnt/myssd
SSD をマウントします:sudo mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/myssd
忘れずに、dev/sdb1 を SSD のパーティション名に置き換えてください。
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-15
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-04
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
これが不可能な場合、または以前のデータを新しいドライブにクローンした場合は、システム BIOS で新しいドライブが起動デバイスとして表示されることを確認し、起動用に選択します。
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-03
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-07
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/topic/update-to-add-native-driver-support-in-nvm-express-in-windows-7-and-windows-server-2008-r2-03cd423b-d42e-66c2-722b-019d16455a6b
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-06
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
BIOS にドライブが存在する場合は、オペレーティングシステム内でディスクを初期化する必要がある場合があります。
Windows の場合:
ステップ 1:ドライブが正しく接続されていることを確認し、システムの電源を入れ、Windows OS を起動します。
ステップ 2:Windows + X を押し、ディスクの管理を選択します。
ステップ 3:SSD が新しく初期化されていない場合、「ディスクを初期化してください」というポップアップが表示されます。
ステップ 4:次のいずれかを選択します。
MBR(マスターブートレコード):2TB 未満のドライブや古いシステムに適しています。
GPT (GUID パーティションテーブル):最新のシステムや 2TB 以上のドライブにおすすめです。
ステップ 5:「OK」をクリックしてディスクを初期化します。
ステップ 6:初期化されると、SSD が「未割り当て」と表示されます。その上で右クリックし、「新しいシンプルボリューム」を選択します。
ステップ 7:画面の指示に従って SSD をフォーマットし、ドライブ文字を割り当てます。
Mac OS の場合:
ステップ 1:ドライブが正しく接続されていることを確認し、システムの電源を入れ、Mac OS を起動します。
ステップ 2:ディスクユーティリティを開きます (Spotlight で Cmd + Space と入力し、「ディスクユーティリティ」と入力すると見つかります)。
ステップ 3:左側のペインで SSD を選択します。
ステップ 4:「消去」をクリックします。
ステップ 5:ドライブの名前を入力し、「フォーマット」で以下を選択します。
新しい Mac および SSD の場合は、APFS。
古いシステムや HDD の場合は、Mac OS Extended(ジャーナル付き)。
ステップ 6:「消去」をクリックします。プロセスが完了すると、SSD が使用可能になります。
Linux の場合:
ステップ 1:ドライブが正しく接続されていることを確認し、システムの電源を入れ、Linux OS を起動します。
ステップ 2:ターミナルを開きます。
ステップ 3:sudo fdisk -l と入力し、接続されているすべてのドライブをリストアップします。SSD のサイズを確認し、デバイス名 (例:/dev/sdb) をメモします。
ステップ 4:fdisk または parted を使って SSD を初期化します。以下は fdisk を使った基本的なガイドです。
sudo fdisk /dev/sdb (/dev/sdb を SSD のデバイス名に置き換えてください) と入力します。
g を押して新しい GPT パーティションテーブルを作成します。
n を押して新しいパーティションを作成します。プロンプトに従ってサイズとタイプを指定します。
w を押して変更を書き込みます。
ステップ 5:SSD 上の新しいパーティションをフォーマットします (例:/dev/sdb1)。お好みのファイルシステムでフォーマットできます。
ext4 の場合:sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
ext3 の場合:sudo mkfs.ext3 /dev/sdb1
FAT32 の場合:sudo mkfs.vfat /dev/sdb1
ステップ 6:SSD をマウントします。
マウントポイントを作成します:sudo mkdir /mnt/myssd
SSD をマウントします:sudo mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/myssd
忘れずに、dev/sdb1 を SSD のパーティション名に置き換えてください。
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-15
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
https://www.kingston.com/blog/pc-performance/two-types-m2-vs-ssd
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-16
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-18
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-14
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-13
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-12
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?
SSD に新しいファームウェアが必要な場合は、ここにある Kingston の SSD Manager ソフトウェアを実行すると通知が表示されます。 www.kingston.com/ssdmanager
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-11
上記の内容はお役に立ちましたか?