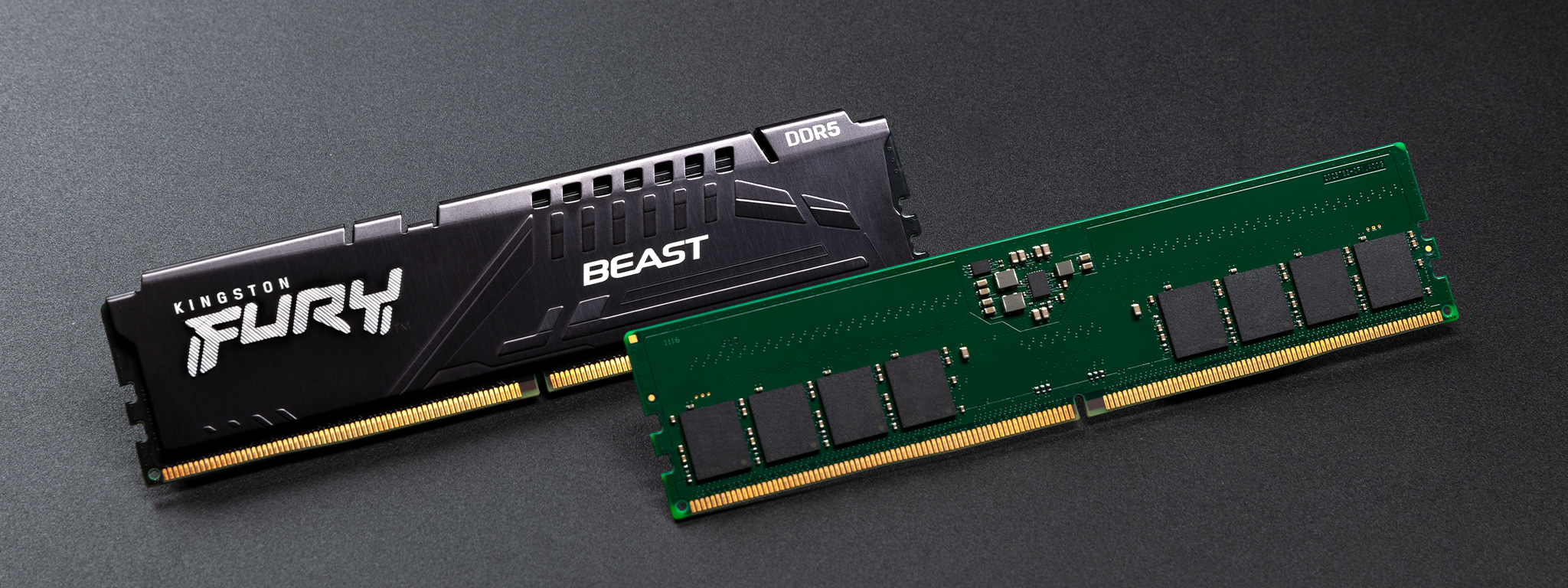
What is MHz?
MHz is short for megahertz and means a million cycles per second, or one million hertz (106 Hz). This unit of frequency measurement comes from the International System of Units, and in computing is used to denote the speed at which data moves within and between components.
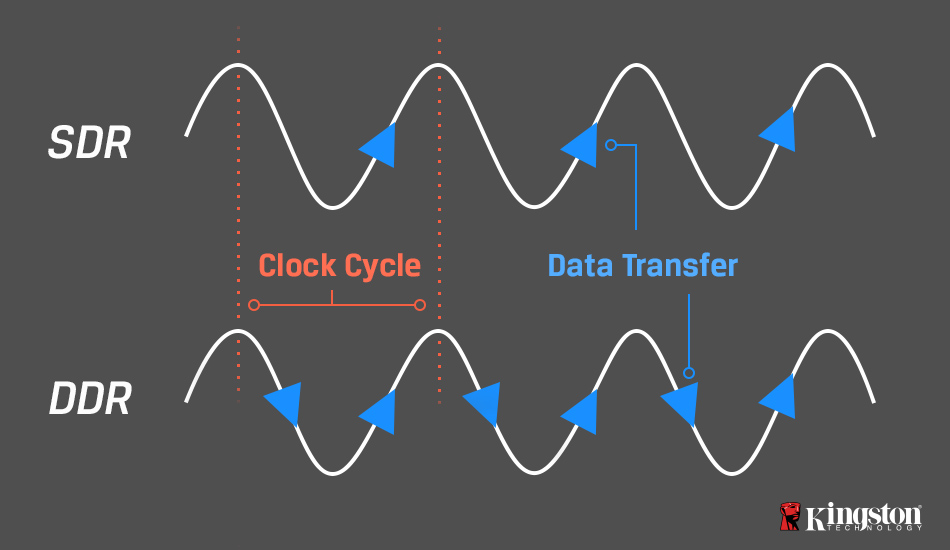
When SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) was introduced in the late 1990s, data transfer speed was measured in sync with the motherboard clock, with data transfers happening on the rising edge of the clock cycle. When measuring performance for SDRAM memory, 100MHz indicated 100 x 106 data transfers per clock cycle.
In the early 2000s, DDR (Double Data Rate) SDRAM memory was introduced. This memory technology doubled the number of data transfers per clock cycle, with transfers happening on the rising and falling edges of the cycle.
The unit of measurement, however, did not change. With a clock rate of 100MHz, DDR doubled the effective data rate at 200 million data transfers with each clock cycle. A new, more accurate description was long overdue.